US12516912 - Lightweight, ballistic and blast-resistant multi-phase composite armor material based on high-toughness heterogeneous interfacial layer and method for preparing the same
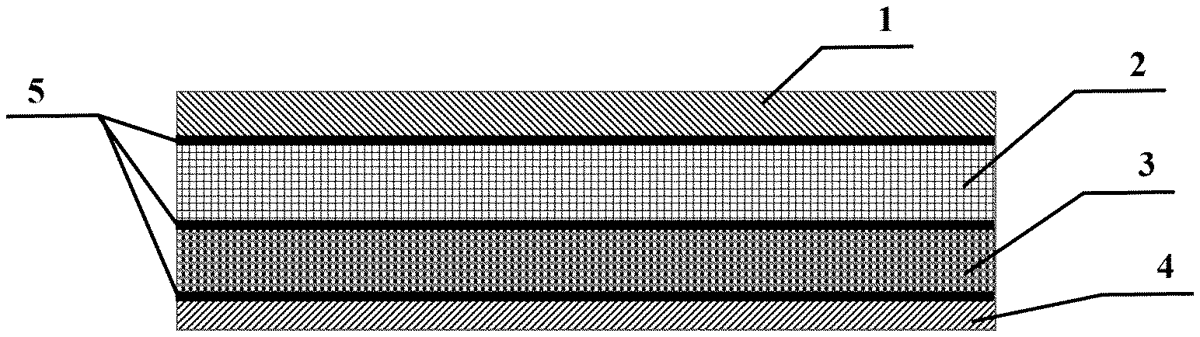
The patent describes a lightweight, multi-phase composite armor material designed for ballistic and blast resistance, featuring layers that include a crack-arresting layer, a bullet-breaking layer, an energy-absorbing layer, and a support layer, all bonded with a high-toughness adhesive film. Each layer serves a specific function, such as stabilizing impact, dissipating energy, absorbing residual energy, and providing structural stiffness, with materials like carbon fiber composites, ceramics, and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene used throughout.
Claim 1
1 . A multi-phase composite armor material, comprising: a crack-arresting layer; a bullet-breaking layer; an energy-absorbing layer; and a support layer; wherein the crack-arresting layer, the bullet-breaking layer, the energy-absorbing layer, and the support layer are arranged in sequence from a bullet-accepting side to the inside; and adjacent two layers of the crack-arresting layer, the bullet-breaking layer, the energy-absorbing layer, and the support layer are bonded with an adhesive film layer; the crack-arresting layer and the support layer are both made of a carbon fiber composite; the bullet-breaking layer is made of ceramic; the energy-absorbing layer is made of an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber composite; and the adhesive film layer is made of a heterogeneous interfacial adhesive; the crack-arresting layer is configured to stabilize an impact region and control a damaged area; the bullet-breaking layer is configured for energy dissipation through fragmentation and expanding an action range of load and energy; the energy-absorbing layer is configured to absorb a residual energy of a bullet; the support layer is configured to provide overall structural stiffness and protect the armor material from being penetrated by a bullet; the adhesive film layer is configured to maintain an overall structural stability of the armor material and allow individual component materials to exert designed performance; and the adhesive film layer is prepared from an epoxy resin system, a short-fiber veil, and a core-shell rubber; wherein the epoxy resin system is prepared through mixing an epoxy monomer or prepolymer, a curing agent, and a reaction promoter and curing. a crack-arresting layer; a bullet-breaking layer; an energy-absorbing layer; and a support layer; wherein the crack-arresting layer, the bullet-breaking layer, the energy-absorbing layer, and the support layer are arranged in sequence from a bullet-accepting side to the inside; and adjacent two layers of the crack-arresting layer, the bullet-breaking layer, the energy-absorbing layer, and the support layer are bonded with an adhesive film layer; the crack-arresting layer and the support layer are both made of a carbon fiber composite; the bullet-breaking layer is made of ceramic; the energy-absorbing layer is made of an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber composite; and the adhesive film layer is made of a heterogeneous interfacial adhesive; the crack-arresting layer is configured to stabilize an impact region and control a damaged area; the bullet-breaking layer is configured for energy dissipation through fragmentation and expanding an action range of load and energy; the energy-absorbing layer is configured to absorb a residual energy of a bullet; the support layer is configured to provide overall structural stiffness and protect the armor material from being penetrated by a bullet; the adhesive film layer is configured to maintain an overall structural stability of the armor material and allow individual component materials to exert designed performance; and the adhesive film layer is prepared from an epoxy resin system, a short-fiber veil, and a core-shell rubber; wherein the epoxy resin system is prepared through mixing an epoxy monomer or prepolymer, a curing agent, and a reaction promoter and curing.
Google Patents
https://patents.google.com/patent/US12516912
USPTO PDF
https://image-ppubs.uspto.gov/dirsearch-public/print/downloadPdf/12516912